NotebookLM and AI Data Automation: A Comprehensive, Practical Guide to Google’s AI Research Tool, Automated Data Entry AI, and Deep Research AI Workflows
In an age where information is abundant but time is scarce, the real competitive advantage is not access to data — it’s the ability to convert that data into reliable, analysis-ready insights rapidly. If you still spend hours copying from PDFs, retyping tables from screenshots, or stitching together research across multiple apps, this guide is for you.
This long-form, practical guide shows how NotebookLM, paired with AI data automation, becomes a modern backbone for research, product decisions, market analysis, and everyday productivity. You’ll learn concrete workflows, ready-to-use prompts, validation best practices, integration tips, and real-world examples that turn theory into repeatable systems. I’ll also explain how NotebookLM interacts with the concepts of a Google AI research tool, automated data entry AI, and Deep Research AI—and how to use them without losing control of accuracy or governance.
Table of contents
- Why NotebookLM matters now
- Core concepts explained: AI data automation, automated data entry AI, Deep Research AI, Google AI research tool
- How NotebookLM works — the architecture and features that enable automation
- Setting up your first NotebookLM data workflow (step-by-step)
- Practical prompt templates (for data tables, chart reverse-engineering, and deep research)
- Case studies: 4 real-world scenarios with outcomes and export examples
- Integration and interoperability: Sheets, CRMs, no-code tools, and pipelines
- Governance, verification, and reliability: how to trust and validate AI outputs
- Advanced tactics: custom personas, batch imports, and chained automations
- SEO, content, and business use: how to monetize your NotebookLM outputs
- Troubleshooting common errors and “failed sources”
- Best-practices checklist and workbook (copyable)
- FAQ — common questions about NotebookLM and AI-driven workflows
- Final thoughts: scaling from one project to organization-wide systems
1. Why NotebookLM matters now
A few trends converge to make NotebookLM uniquely useful in 2025–2026:
- Data fragmentation: important details live in PDFs, images, private docs, and webpages. Extracting them manually wastes hours.
- Tool maturity: models and OCR have improved enough that extracting structured numbers from messy inputs is practical and cost-effective.
- No-code momentum: business users want automation without engineering overhead.
- Persistent knowledge: teams need systems that remember sources, not ephemeral chat sessions.
NotebookLM sits at the intersection of these trends: it’s a Google AI research tool built to hold, analyze, and output structured knowledge. Instead of short-lived chatbot answers, it gives you reproducible tables, export paths, and persistent notebooks that become your project’s single source of truth.
2. Core concepts explained
Before jumping into workflows, let’s align on key terms and what they practically mean.
NotebookLM
An interactive notebook experience (from Google) that ingests documents, images, and URLs, preserves sources, and generates structured outputs such as tables, timelines, and summaries. It’s designed for long-running research, document-first reasoning, and repeatable outputs.
AI data automation
A workflow pattern where AI is used to read, extract, normalize, and export data automatically — minimizing manual data entry and reducing friction between unstructured inputs and structured outputs.
Automated data entry AI
A focused subtype of AI data automation: the automation of converting document fields and image contents into rows and columns suitable for spreadsheets, CRMs, and databases.
Deep Research AI
A capability that goes beyond the uploaded sources: the system discovers additional relevant sources, cross-references them, evaluates credibility, and enriches the dataset. It’s research at scale but with traceability.
3. How NotebookLM works — the engine behind automation
At a high level, NotebookLM combines several capabilities:
- Multimodal ingestion — PDFs, images, plain text, and links are converted into machine-readable form (OCR + parsing).
- Source-aware reasoning — answers reference and link back to source documents, so every extracted fact is traceable.
- Data table generation — the system can propose and generate structured tables from heterogeneous inputs.
- Deep Research — the notebook can optionally expand its knowledge set by finding new sources, then re-running extraction to deliver a richer table.
- Export & interop — one-click export to Google Sheets, CSV, or copy-pasteable tables.
This combination turns a one-off extraction job into a reproducible pipeline: you can rerun a notebook when new documents arrive and the system will update tables while preserving provenance.
4. Setting up your first NotebookLM data workflow (step-by-step)
Below is a pragmatic, repeatable setup that many analysts use. Replace the example files and prompts with your own.
A. Define the outcome
Decide the table you want. Example: “A lead table with columns — Name, Email, Company, Job Title, Submission Date, Notes, Source URL.”
B. Create a notebook
Open NotebookLM, create a new notebook and name it for the project (e.g., “2026 Vendor Survey Extraction”).
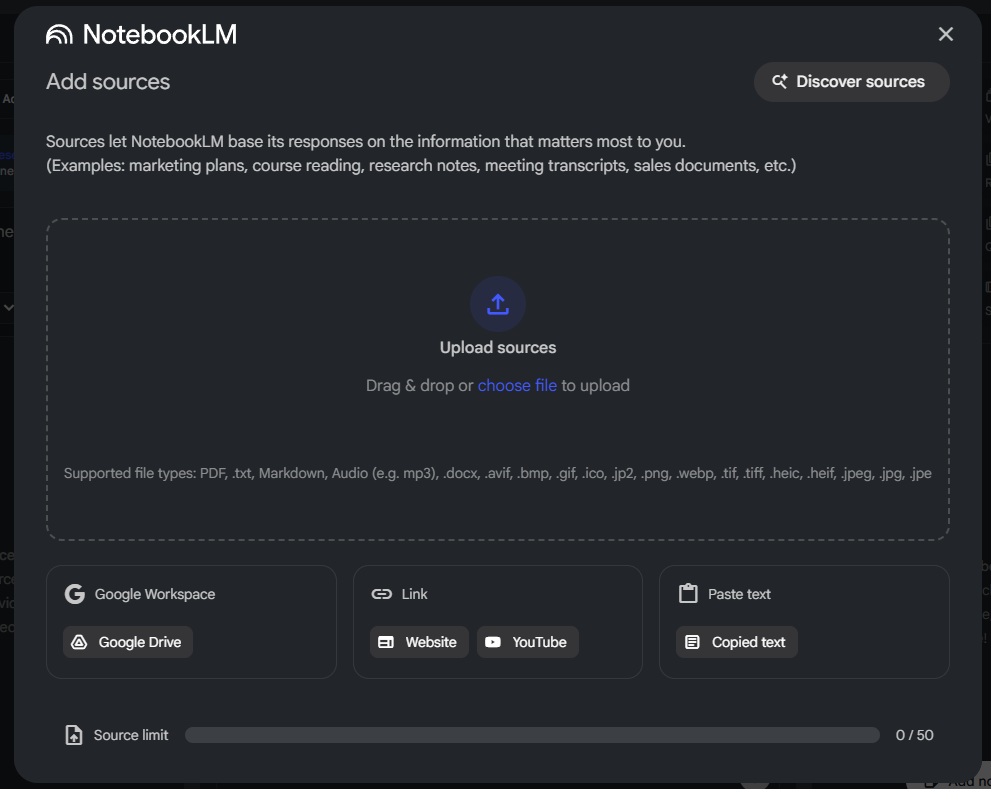
C. Upload sources
Add batches of:
- PDFs (filled forms, contracts)
- Images (screenshots of charts)
- URLs (web research)
Label them with consistent names — later the notebook will display the source name in a column.
Keep in mind the limit of Upload source as you can see in bottom section of image
D. Start the Data Table extraction
Use the Data Table feature and give a clear instruction:
“Extract all contact fields from these documents into a table with columns: Name, Email, Company, Job Title, Submission Date, Notes, Source. Normalize dates to YYYY-MM-DD.”
E. Review & refine
NotebookLM generates a draft table. Scan first 10 rows, check formatting, correct a column example (if date formats vary), then re-run. Use the Edit icon to give clarifying rules.
F. Export or pipeline it
Once satisfied:
- Click “Export to Google Sheets” or
- Export CSV and import to your CRM (via Zapier/Make/Make.com), or
- Use a no-code tool to schedule periodic imports for new docs.
5. Practical prompt templates
Below are clean, effective prompt templates you can paste into NotebookLM’s edit box to get precise outputs.
5.1 Extracting form fields from PDFs
“Extract all fields from uploaded PDF forms. Create columns: Full Name, Email, Phone, Organization, Role, Country, Submission Date, Free-text Notes. Standardize date formats to YYYY-MM-DD. Put the source filename in
Sourcecolumn. If a field is empty, leave the cell blank.”
5.2 Reverse-engineering charts from screenshots
“Convert this chart image into a data table. Identify the X-axis labels (dates) and Y-axis values. Produce columns: Date, Value. Estimate values when exact numbers aren’t printed. Add a
Confidencecolumn with values High/Medium/Low and explain any assumptions in the Notes column.”
5.3 Deep Market Research list
“Act as a procurement analyst and find suppliers for [product]. For each result, create columns: Supplier Name, Country, Contact, Price (local currency), MOQ, Website, Notes, Source URL. Rate
Suitabilityon a 1–5 scale based on price and shipping availability.”
5.4 Batch normalization rules
“Normalize phone numbers to E.164 when possible. Remove duplicate rows, keeping the entry with the most filled fields. Convert all currency fields to USD using the exchange rate at the time of the source (add
ExchangeRateDatecolumn).”
6. Case studies — real-world scenarios
Case study A: Non-profit volunteer intake
Problem: A non-profit receives volunteer forms as PDFs and emails. Volunteers must be added to the database quickly.
Workflow: Upload all PDFs to NotebookLM, extract contact fields using a Data Table, export to Google Sheets, run a Sheets script to deduplicate, import into Mailchimp.
Outcome: Time to onboard volunteers reduced from hours to under 20 minutes per batch. Error rates dropped because the AI standardized addresses and dates.
Case study B: Market pricing comparison for procurement
Problem: Procurement team needs fast comparisons across dozens of local suppliers with screenshots and PDF catalogs.
Workflow: Use Deep Research to find additional supplier pages, extract price columns into a single table, convert all prices to local currency automatically, add Suitability rating.
Outcome: Procurement eliminated manual spreadsheet assembly and gained a sortable, filterable dataset that enabled a 12% cost-saving on the first tender.
Case study C: Academic literature review
Problem: Grad students must extract experimental parameters and results from 200 papers.
Workflow: Upload PDFs, instruct NotebookLM to create columns for sample size, method, metrics, and key findings. Use Deep Research to fetch supplementary data linked from articles.
Outcome: The literature review transformed from weeks of manual extraction into a reproducible notebook that powers a living literature table.
Case study D: Productized consulting deliverable
Problem: A solo consultant needs to deliver a competitive analysis report with 30 competitors, screenshots, pricing tables, and summaries.
Workflow: Extract data, generate comparison table, ask NotebookLM to draft the executive summary and generate charts via export to Sheets.
Outcome: The consultant delivered a premium report in a day, scaled the process into a 2-hour repeatable product, and increased client throughput.
7. Integration and interoperability
NotebookLM is most powerful when it is an organ in a larger stack rather than a silo.
Common integrations
- Google Sheets — one-click export for deeper analysis, pivot tables, and charts.
- Zapier / Make (Integromat) — for triggering workflows when new exports appear.
- CRMs (HubSpot, Pipedrive) — import contact tables via CSV or API.
- No-code sites (Airtable, Bubble) — load structured data as records.
- BI tools (Looker, Google Data Studio, PowerBI via CSV) — for dashboarding.
Example pipeline
- NotebookLM outputs a CSV to Google Drive.
- A scheduled Zap triggers when a new CSV appears.
- Zap parses CSV and upserts into your CRM.
- CRM triggers welcome emails and onboarding tasks.
This way you get human oversight at extraction and automation in downstream systems.
8. Governance, verification, and reliability
Automation is powerful—but it must be trustworthy.
Validation layers
- Source citation — always enable NotebookLM’s
Sourcecolumn. Use it to audit suspect rows. - Confidence flags — add a
Confidencecolumn. Low-confidence rows should be human-checked. - Sampling — for every extraction run, manually review a random sample (e.g., 5–10%) of rows to measure precision and recall.
- Duplication rules — define dedupe logic (e.g., by email + normalized name).
- Change logs — keep a versioned export of tables so you can trace changes.
Legal & privacy
- Don’t upload documents with private personal data unless you have a legal basis to process them.
- Maintain secure storage and access controls for exported spreadsheets.
- If you’re dealing with regulated data (financial, health), run an additional compliance review.
9. Advanced tactics
Custom personas
Train NotebookLM to adopt a specific tone or role (e.g., “Act as a procurement analyst with 10 years of experience in electronics sourcing”) to get extraction rules tuned to domain-specific requirements.
Batch imports + templates
Create document naming conventions and an import template so the notebook applies consistent parsing rules. For recurring jobs, clone the notebook and swap the input folder.
Chained automations
Use NotebookLM extraction → Sheet formulas → Apps Script to transform and enrich → Push to API. The notebook handles the heavy lifting of extraction; your scripts handle deterministic transformations.
10. SEO, content, and business use
NotebookLM isn’t just a research tool; it’s a content and business accelerator.
- SEO research: extract competitor headings, meta descriptions, and content structure into a table for pattern analysis.
- Content repurposing: extract quotes, statistics, and fact sources to populate an article or slide deck.
- Products & pricing: build product catalogs from supplier PDFs for quick e-commerce setup.
- Monetizable services: offer “data extraction” as a service to customers who need clean spreadsheets from messy inputs.
11. Troubleshooting common errors
Problem: Dates parse inconsistently.
Fix: Add explicit normalization rules in your prompt and include examples: “Convert May 1, 2025 and 01/05/25 to 2025-05-01.”
Problem: Chart OCR misses axis labels.
Fix: Re-upload a higher-resolution image; add context describing the units and axis orientation.
Problem: Duplicate rows appear.
Fix: Set deduplication logic and specify a primary_key (e.g., email or URL + timestamp).
Problem: Deep Research returns irrelevant sources.
Fix: Narrow the query with domain lists or specific keywords, and instruct NotebookLM to exclude pages older than X years.
12. Best-practices checklist & workbook (copy/paste)
Before upload
- Remove unnecessary pages from PDFs
- Rename files with consistent format:
YYYYMMDD_source_topic.pdf - Create a project notebook and name it clearly
Extraction prompt basics
- Define explicit columns
- Provide normalization rules
- Add dedupe logic
- Ask for a
Confidencecolumn andSource
Post extraction
- Validate 5–10% random sample
- Export to Google Sheets and run automated checks (formulas)
- Archive original notebook exports with timestamp
13. FAQ
Q: Can NotebookLM handle handwritten notes?
A: Yes — modern OCR is quite capable, though accuracy depends on handwriting clarity. Always set a Confidence flag and human-verify low-confidence rows.
Q: Is Deep Research AI safe for sensitive projects?
A: Deep Research fetches public sources. Don’t rely on it for private data. For sensitive matters, limit searches to trusted domains and skip Deep Research.
Q: How accurate is automated data extraction?
A: High for typed text and printed forms, variable for images and handwriting. Accuracy improves with clearer inputs and carefully specified prompts.
Q: Does NotebookLM replace data engineers?
A: No. It reduces manual ETL work and speeds prototyping. Complex data pipelines and enterprise-scale governance still require engineers.
14. Final thoughts: scaling from one project to organization-wide systems
NotebookLM and the surrounding field of AI data automation change the economics of information work. Tasks that once required staff hours or contractor budgets can be moved into reproducible AI notebooks that produce consistent, auditable outputs.
To scale:
- Start small and iterate on prompts.
- Build templates for recurring jobs.
- Add validation layers and governance early.
- Integrate with simple automation tools (Zapier/Make) before building heavy engineering.
If you treat NotebookLM as a component in a larger automation stack, rather than a magic box, you’ll gain the benefits of speed while keeping control of quality and compliance.


